A Brief History: Who Developed Semi-Supervised Scenarios? The concept of semi-supervised learning (SSL) was introduced in the late 1990s to address the growing need to utilize unlabeled data in machine learning. Researchers like Xiaojin Zhu pioneered frameworks for combining labeled …
Imagine separating apples and oranges on a table where only a few are labeled requires educated guesses about the rest. Semi-Supervised Support Vector Machines (S3VMs) work similarly: they combine a small set of labeled data with a larger pool of …
Imagine you’re throwing darts at a dartboard: if your darts consistently miss the center but land in a tight cluster, your aim has a bias—it’s systematically off-target. Similarly, the bias of an estimator measures how far an estimation method deviates …
A Brief History of This Tool: Who Developed It? Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) originated in the 1960s as a statistical framework for analyzing sequential data. Leonard E. Baum and his team pioneered this groundbreaking methodology. Over time, libraries like hmmlearn …
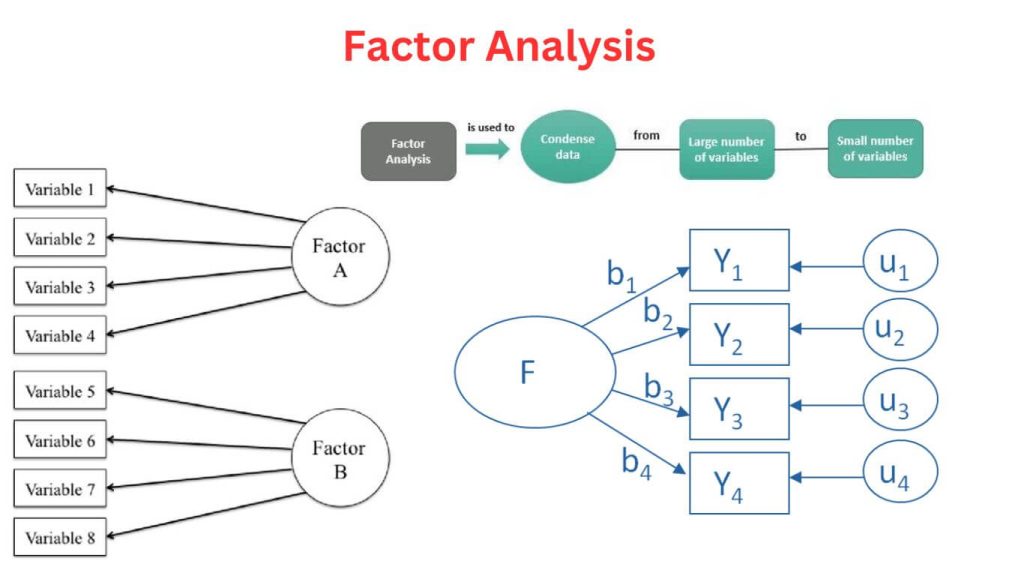
A Brief History: Who Developed Factor Analysis? The history of factor analysis traces back to Charles Spearman, who introduced it to study intelligence in the early 20th century. Since then, this statistical method has become a foundational tool in fields …
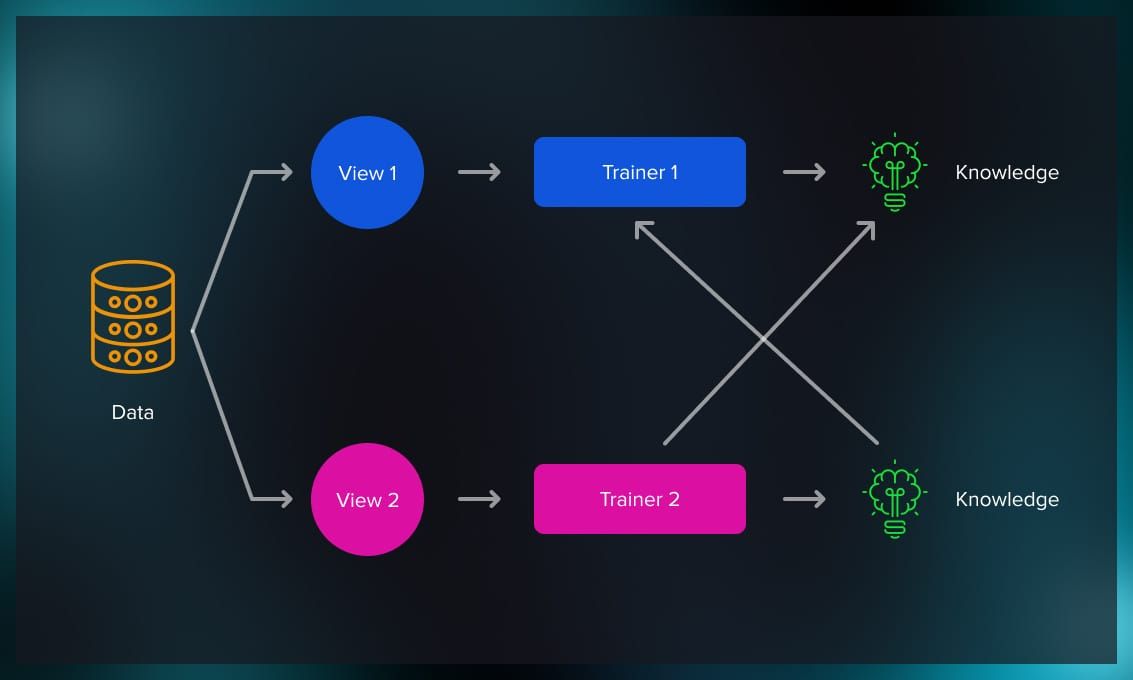
A Brief History of This Tool Label propagation, a machine learning algorithm for semi-supervised learning, was first introduced to leverage both labelled and unlabelled datasets for enhanced predictions: researchers in statistical physics and computer science, such as Xiaojin Zhu, significantly …
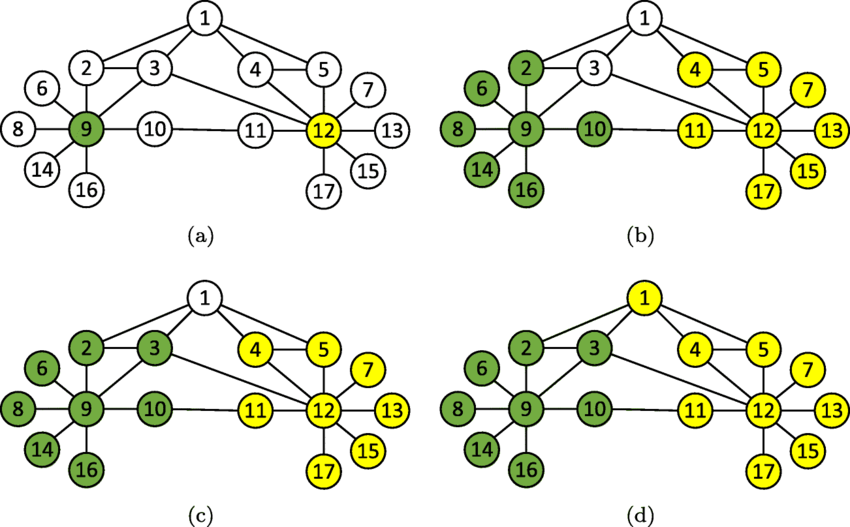
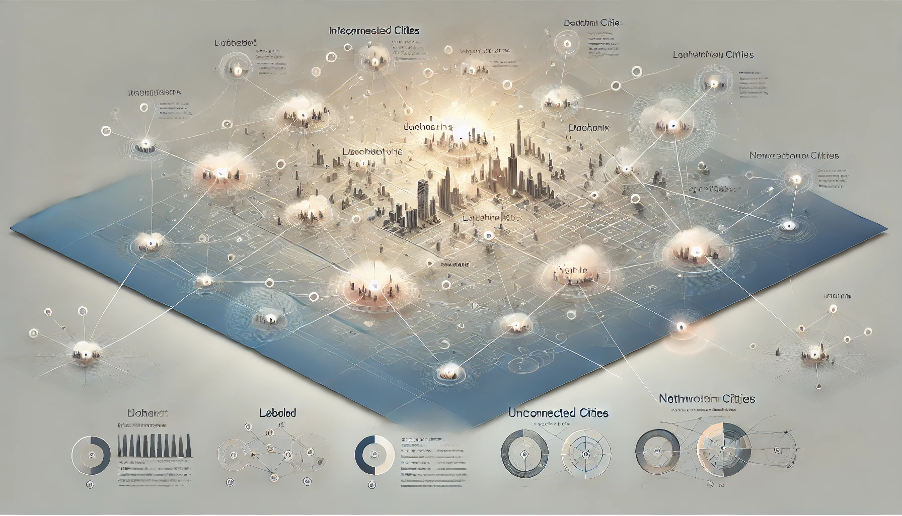
Introduction Picture a map of interconnected cities. You know the names of a few cities, and their connections help you understand the others. Graph-Based Semi-Supervised Learning (GBSSL) follows a similar principle: it uses labelled and unlabelled data points connected in …
Imagine you’re baking a cake for a competition: you test the recipe multiple times at home before presenting the final version to the judges. The home trials are like the training set, where you perfect your recipe, while the competition …
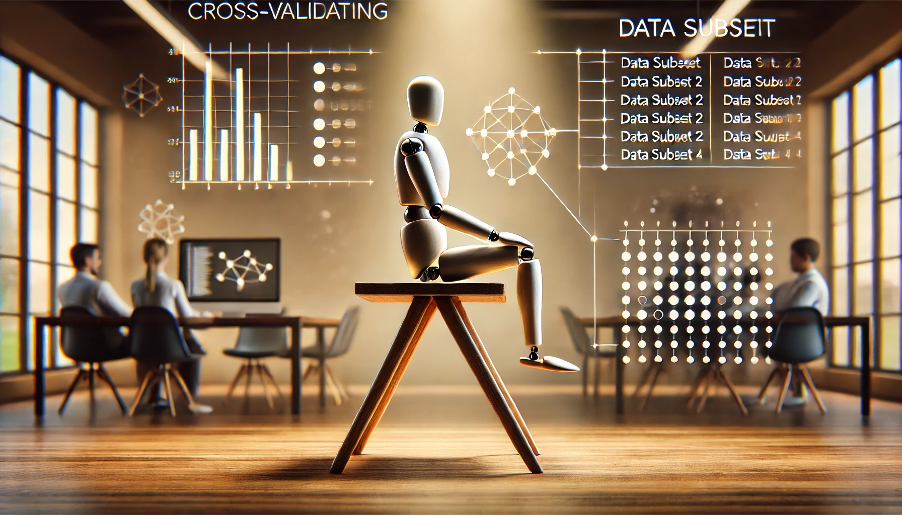
Imagine you’re testing the strength of a chair: instead of sitting on it just once, you test each leg to ensure stability. Cross-validation works similarly in machine learning workflows: it evaluates a model’s reliability by testing it on multiple subsets …
Separating clusters of dots on a page when only a few are labelled requires precision. Transductive Support Vector Machines (TSVMs) do just that: they combine labelled and unlabelled data to find the best classification boundary, optimizing for the current dataset. …