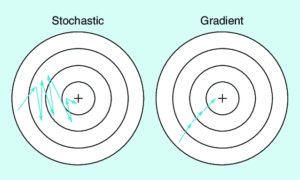
A Very Short Introduction of Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD) is a foundational optimisation algorithm that improves machine learning efficiency by processing small data subsets. Widely used in industries like healthcare, urban planning, and climate forecasting, SGD ensures scalable and robust model training.