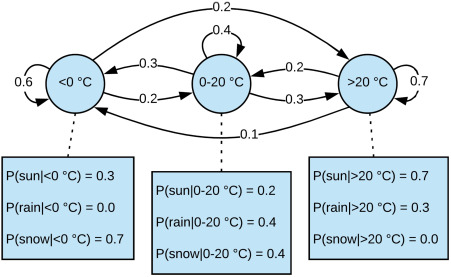
A Brief History: Who Developed Hidden Markov Models (HMMs)?
Hidden Markov Models were introduced in the 1960s by Leonard E. Baum and colleagues. These models have become pivotal in various industries, from speech recognition to bioinformatics, thanks to their adaptability and predictive accuracy.
What Is an Addendum to HMMs?
An addendum to HMMs enhances the framework, enabling it to solve modern computational challenges. Picture it as upgrading a versatile toolkit with specialized tools, allowing greater precision and efficiency for specific tasks.
Why Are Addendums to HMMs Used? What Challenges Are Addressed?
Addendums address gaps in traditional HMMs while expanding their application:
- Scalability: Efficiently managing large datasets.
- Noise Handling: Improving accuracy with incomplete or noisy data.
- Customization: Adapting for industry-specific needs like fraud detection or sentiment analysis.
These upgrades enable HMMs to stay relevant in fast-evolving industries.
How Are Addendums to HMMs Used?
Addendums integrate into workflows to optimize outcomes:
- Time Evolution Models: Adapting to dynamic systems like market trends.
- Hybrid Models: Combining HMMs with neural networks for superior predictions.
- Custom State Design: Tailoring states to specific domains, such as ecological monitoring.
Think of addendums as modular upgrades for a GPS system, fine-tuning it for complex terrains.
Different Types of Addendums to HMMs
- Continuous HMMs: For continuous observation data.
- Hidden Semi-Markov Models: Incorporate time-based transitions.
- Hierarchical HMMs: Useful for multi-level tasks requiring nested structures.
Key Features of HMM Addendums
- Domain Adaptability: Tailored solutions for diverse industries.
- Enhanced Accuracy: Robust against uncertainty and noisy datasets.
- Seamless Integration: Compatible with advanced libraries like TensorFlow.
Popular Software for Addendums to HMMs
- Scikit-learn: Simple implementation of foundational HMM features.
- TensorFlow Probability: Advanced probabilistic modeling.
- PyMC3: Bayesian parameter estimation for flexible applications.
Applications in Australian Government Agencies
- Healthcare: Patient journey prediction for resource allocation.
- Transport: Modeling urban traffic for optimized planning.
- Climate Science: Analyzing weather patterns for policy-making.
How interested are you in uncovering even more about this topic? Our next article dives deeper into [insert next topic], unravelling insights you won’t want to miss. Stay curious and take the next step with us!